Combination of List.Accumulate and Table.CombineColumns Function to combine columns
- V E Meganathan
- Jun 3, 2025
- 1 min read
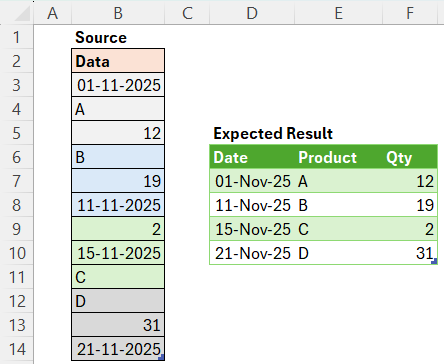
Trick to combine set of columns in a table:

Our dataset includes the Price and Quantity of Fruits for each quarter.
We need to compute the sales number of Fruits for every quarter.
I will demonstrate a technique that combines the List.Accumulate Function with the Table.CombineColumns Function.
let
Source = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Table1"]}[Content],
Result = List.Accumulate(List.Split(List.Skip(Table.ColumnNames(Source)),2), Table.Skip(Source), (s,c) => Table.CombineColumns(s,c,each List.Product(_),c{0}))
in
Result
Combine Different Number of Columns Across Multiple Groups in a Single Step - Power Query:

In a previous method, we covered how to combine pairs of columns in Power Query. In this method, we will focus on combining columns into several groups, where the number of columns in each group may differ.
The source data includes Product Sales information for every Customer and Organization.
Products Q, R, and T have 3, 2, and 4 columns, respectively.
We need to combine the columns of each product and compute the total sales.
let
Source = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Table1"]}[Content],
Result = List.Accumulate(List.Distinct(List.Transform(List.Skip(Table.ColumnNames(Source),2), (f) => Text.End(f,1))), Source,(s,c) => Table.CombineColumns(s, List.Select(Table.ColumnNames(Source), each Text.EndsWith(_,c)), each List.Sum(_), c & "-Sales" ))
in
Result





Comments